exc-5b28d897562fa787237817d5


Blockchain is lauded as having the potential to transform the global economy due to its ability to increase transparency and trust. Why? Blocks of information (time-stamping of life events or financial transactions) are secured by complex algorithms that are hard to hack and cannot be erased or manipulated. Therefore, it has a huge role to play in validating identity management, without the use of an independent third party. It can verify that we are who we say we are and the goods we are buying are what they claim to be.
The benefits of blockchain are now going beyond the world of finance into other industries, including education, where trust is essential. The Blockchain in Education report by the Joint Research Council of the European Commission, is an exploratory review of the technology and its potential applications within Europe. It demonstrates how seriously the technology is being taken in the education space.
More than a digital diploma
The increasingly fickle nature of employment means that more qualifications are needed as career paths deviate across organisations and disciplines. Often qualifications are obligatory just to be able to apply for a role, and with increased demand, educational dishonesty is on the rise. However, blockchain has the ability to be the backbone of educational proof, giving employers the information required to determine whether a candidate’s CV is accurate. Crucially, technology can determine if qualifications needed to get that all important foot in the door for a dream job are valid.
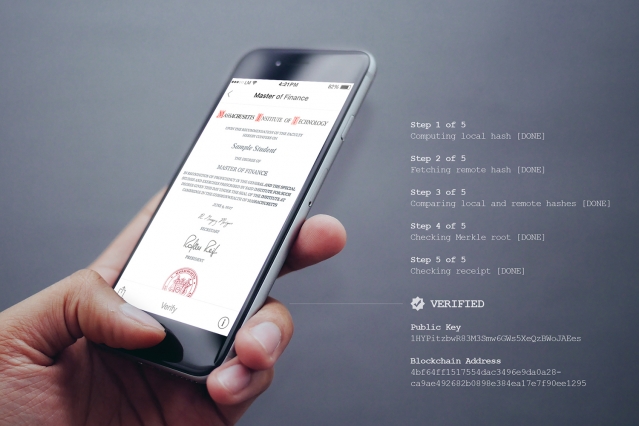
Over in the US, MIT is already making waves with blockchain technology. Last summer, as part of a pilot programme, over 100 graduates could receive their diplomas in digital format via an app in addition to the traditional paper-based format. Although there will always be a place for tradition, certificates issued through the app, called Blockcerts Wallet, allow graduates to securely share a verifiable and tamper-proof digital version of their diplomas with prospective employers and other institutions. The parallels to Bitcoin are easy to deduce: a digital token represents the credentials and qualifications can be added to the app, providing both a digital diploma and instant verification of authenticity.
The portal essentially uses the digital ledger to locate the transaction ID (identifying when the digital record was added to the blockchain), verifying the keys, and confirming that nothing has been altered since the record was added. As each certificate or diploma is logged as a transaction on the blockchain network, it prevents tampering or fraud.
There are many more examples emerging of universities offering digital credentials via blockchain or of new educational companies, such as Gradbase, which offer instantaneous verification of academic records. In fact, University College London has been using Gradbase to issue degree certificates for some courses. The student, or owner of the qualification, receives a QR code which they can include on their CV and LinkedIn profile. Employers can then easily verify the authenticity of educational credentials.
The Knowledge Media Institute (KMI) within the Open University is also experimenting with improving standards for certification and the wider use of blockchain technology within education. It is working with APPII – a Blockchain career verification platform – to build a platform that can register and verify student academic records. With its history of providing flexible distance learning courses, the Open University has over 170,000 students using its own core open learning platform. Therefore, the potential to develop a blockchain strategy to classify all courses within the university could help to lower costs and enhance validity of the qualifications achieved.
Smart learning
With lifelong learning more important than ever as employees face a constant need to improve their skills, education systems and recruitment processes need to be more efficient and immersive to adapt to different demands. This is why blockchain has great potential in the education sector. It can allow workers to build up a secure, verifiable digital record of formal qualifications, experience and soft skills gained over their lifetime. In addition, by using a smart contract, blockchain applications could provide students with the ability to gain greater control over their individual education through offering flexible access to content and courses suggested based on previous successes or failures and attainment.
Blockchain is still a developing technology, but we are already seeing real world benefits. Education is a multi-faceted sector where different systems need to adapt to prepare students for the jobs of tomorrow. Having a fool proof system that records a student’s academic history before and during a working life can not only help in battling dishonesty, but can also help to tackle the issues of bespoke learning. This will ultimately give people the best chance of determining their education path and a successful future career.
Denver, Colorado, 24th February 2025, Chainwire
Denver, Colorado, 20th February 2025, Chainwire
Washington, D.C., 18th February 2025, Chainwire
Dubai, UAE, 27th January 2025, Chainwire
Those who enter the market at this time may be surprised to hear that Bitcoin…
George Town, Grand Cayman, 22nd November 2024, Chainwire