Cryptocurrency arbitrage is the simultaneous purchase and sale of a cryptocurrency to profit from an imbalance in price. It is a trade that profits by exploiting the price differences of the same asset on different cryptocurrency exchanges.
Cryptocurrency arbitrage can only exist as long as markets are not perfect. For example, an arbitrage opportunity is present when there is the opportunity to instantaneously buy something for a low price on one market and sell it for a higher price somewhere else.
There are two major kinds of crypto arbitrage:
- Arbitrage between exchanges
- Arbitrage within a single exchange
Let’s have a look at both of them and consider the pros and cons.
Inter-exchange arbitrage
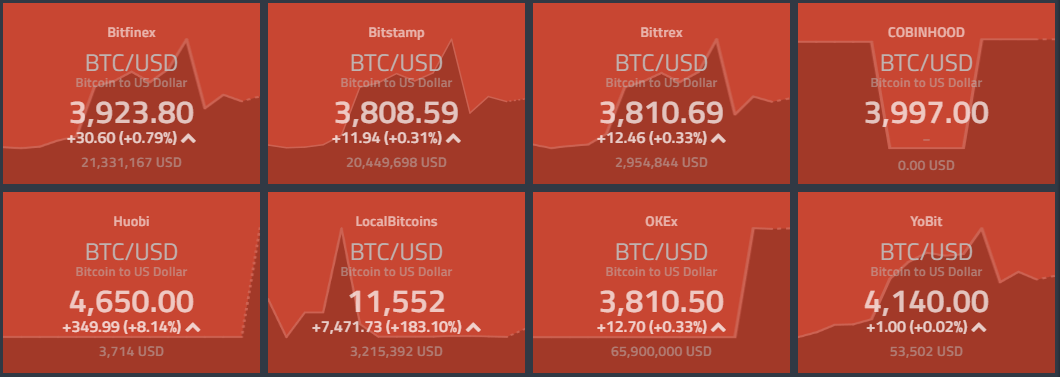
Cryptocurrency arbitrage between different exchanges is the most obvious type of arbitrage, because it is very similar to fiat currency arbitrage (forex arbitrage) and sports arbitrage. The idea is simple: benefit from the differences in prices for the same coin but on different exchanges. For example, take a look at the different prices for Bitcoin in US dollars on different exchanges in the image above, where the price for 1 Bitcoin ranges between $3,808 and $11,552. In this example, you could profit from a 303% spread between exchanges by purchasing Bitcoin at $3,808 and selling at $11,552.
Identifying arbitrage opportunities
To identify great cryptocurrency arbitrage opportunities between exchanges, a few factors need to be taken into account, such as:
- Liquidity: As in the difference in the trading volumes on different exchanges, as the difference in supply and demand affects the prices. On more established exchanges, prices fluctuate less than on smaller or new ones.
- Geography: Depending on the time-zone, it might be easier or harder to sell during certain times of the day.
- Listings: As in the price difference when a crypto coin gets listed on one of the major exchanges, like Binance vs Bybit.
How to benefit from cryptocurrency arbitrage
- Register on both exchanges of your choice
- Deposit fiat on one exchange and buy a Bitcoin or any other cryptocurrency
- Transfer your cryptocurrency to the other exchange
- Sell your crypto asset for fiat
- Withdraw the profit
The first catch is that traders usually need to pay trading and withdrawal fees, which can be as little as 3% of your crypto asset price or as much as 15% depending on the exchanges used.
The second catch is that the transfer between exchanges can take up to five days. Since the volatility of cryptocurrencies is high, the theoretical profit might diminish during this time (or increase).
It is possible to reduce the amount of fees and also waiting time by depositing both crypto and fiat currency in both exchanges you wish to use for arbitrage opportunities. With this method, there is no transfer of the cryptocurrencies between exchanges, which means reduced waiting times. However, the withdrawal fees are still in place when you decide to cash out your profits.
Intra-exchange arbitrage
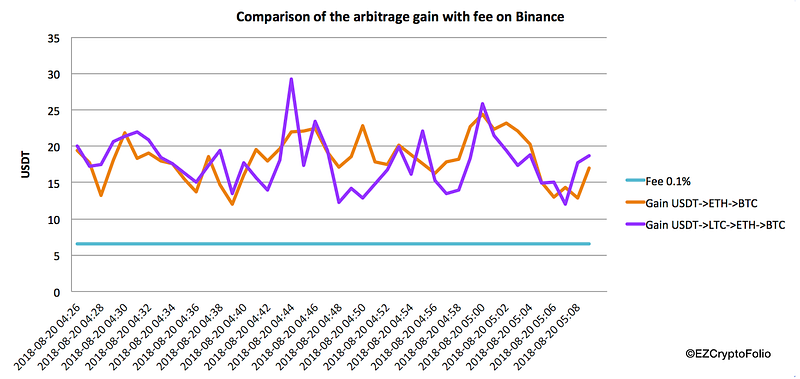
Arbitrage within a single exchange is similar to triangular arbitrage, also known as cross-currency arbitrage. This type of arbitrage is mostly associated with forex trading. The step-by-step process to make a profit with intra-exchange arbitrage is as follows:
- Start by depositing some fiat on an exchange
- Buy cryptocurrency A
- Sell cryptocurrency A for cryptocurrency B
- Repeat steps two and three
- Sell cryptocurrency B for fiat (USD, USDT)
- Withdraw profits
In essence, you could substitute fiat with yet another cryptocurrency, or repeat step two many times with different cryptocurrencies. In the latter case, it will no longer be triangular arbitrage, but polygonal arbitrage. Of course, the probability of diminishing returns increases with each further step, meaning traders should be wary and take the time to properly measure risk/reward.
By staying within a single exchange and applying the same process over and over again to different cryptocurrencies, the major fee (withdrawal of cryptocurrency) is eliminated.
The catch in this case, though, is that the opportunity is less obvious than in the case of arbitrage between exchanges, and additional steps need to be taken.
What next?
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by the author should not be considered as financial advice. We do not give advice on financial products.